Writers: HERRERA, A.; FERNANDES, R. G.; CAMARGO, Andrea Simone Stucchi de; HERNANDES, Antonio Carlos; BUCHNER, S.; JACINTO, C.; BALZARETTI, N. M.
Keywords: Photoluminescence; oxide; glass
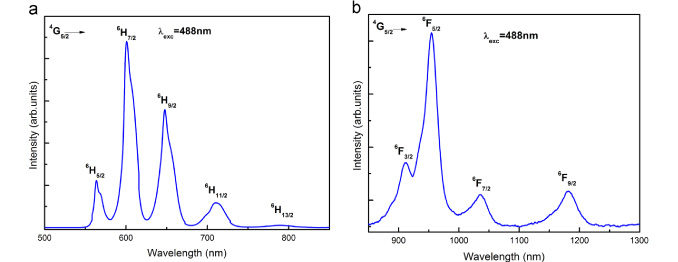
Abstract: A highly transparent Sm3+ glass with composition B2O3–PbO–Bi2O3–GeO2 was obtained by the traditional melt quenching technique and characterized from structural and spectroscopic points of view. Analysis by X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy confirmed the amorphous nature of the sample and revealed the expected low phonon energy. Differential thermal analysis was also carried out to obtain the glass transition and the crystallization temperatures, related to the thermal stability of the sample. Judd–Ofelt theory was applied to evaluate phenomenological intensity parameters Ωλ (λ=2, 4 and 6) from the optical absorption measurements. The transition probabilities, radiative lifetimes, branching ratio and stimulated emission cross-section were also calculated. Photoluminescence spectra recorded in the visible and infrared regions revealed intense green, orange, red and near infrared emission bands providing a new trace to develop tunable laser and optoelectronics devices.