Writers: Débora Cristina Damasceno, Hellen Pontes Silva, Geizi Fátima Vaz, Francine Aparecida Vasques-Silva, Iracema Mattos Paranhos Calderon, Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge, Kleber Eduardo Campos, Gustavo Tadeu Volpato
Keywords: exercise; diabetes mellitus; pregnancy; reproductive outcome; anomaly
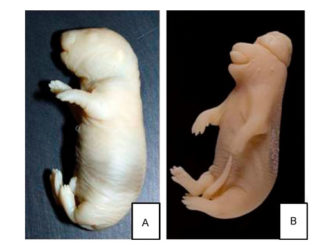
Abstract: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of exercise prior to or during pregnancy on maternal reproductive outcome, biochemical profile, and on fetal anomaly frequency in a rat pregnancy model utilizing chemically induced diabetes. Wistar rats (minimum n = 11 animals/group) were randomly assigned the following groups: group 1 (G1), sedentary, nondiabetic; G2, nondiabetic, exercised during pregnancy; G3, nondiabetic, exercised prior to and during pregnancy; G4, sedentary, diabetic; G5, diabetic, exercised during pregnancy; and G6, diabetic, exercised prior to and during pregnancy. A swimming program was utilized for moderate exercise. On day 21 of pregnancy, all rats were anesthetized to obtain blood for biochemical measurements. The gravid uterus was weighed with its contents, and the fetuses were analyzed. The nondiabetic rats exercised prior to pregnancy presented a reduced maternal weight gain. Besides, G2 and G3 groups showed decreased fetal weights at term pregnancy, indicating slight intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). In the diabetic dams, the swimming program did not have antihyperglycemic effects. The exercise applied only during pregnancy caused severe IUGR, as confirmed by reduced fetal weight mean, fetal weight classification, and ossification sites. Nevertheless, exercise was not a teratogenic factor and improved the rats’ lipid profiles, demonstrating that the exercise presented possible benefits, but there are also risks prior and during pregnancy, especially in diabetic pregnant women.
DOI: 10.1177/1933719112461186