Writers: Anderson R. Albuquerque; Jefferson Maul; Elson Longo; Iêda M. G. dos Santos; and Julio R. Sambrano.
Keywords: Applied pressure; Density of state; Electronic and structural properties; Uniaxial pressures; Vibrational properties; Dispersions; Hydraulics; Hydrodynamics; Titanium dioxide
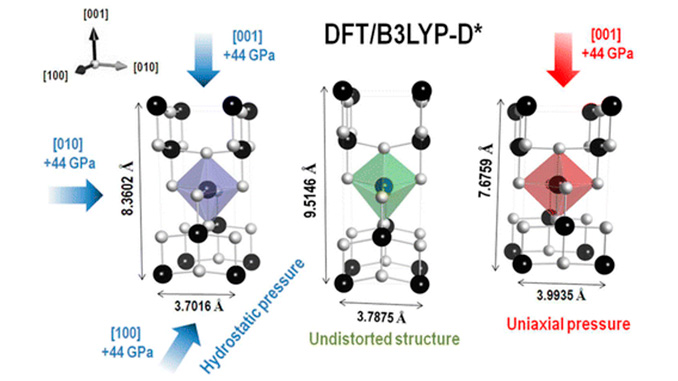
Abstract: The effect of high hydrostatic and [001] uniaxial pressures on TiO2 anatase was studied under the framework of periodic calculations with the inclusion of DFT-D2 dispersion potential adjusted for this system (B3LYP-D*). The role of dispersion in distorted unit cells was evaluated in terms of lattice parameters, elastic constants, equation of state, vibrational properties, and electronic properties (band structure and density of states). A more reliable description at high pressures was achieved because the B3LYP-D* presented an improvement in all properties for undistorted bulk over conventional B3LYP and B3LYP-D. From density of states analysis, we observed that the contribution of crystalline orbitals to the edge of valence and conduction bands changed within applied pressure. The studied distortions can give some insight into behavior of electronic and structural properties due to local stress in anatase bulk from doping, defects, and physical tensions in nanometric forms.