Writers: Vinícius D. Araújo, Maurício M. de Lima Jr., Andrés Cantarero, Maria I.B. Bernardi, Jorge D.A. Bellido, Elisabete M. Assaf, Rosana Balzer, Luiz F.D. Probst, Humberto V. Fajardo
Keywords: Ceramics; Chemical synthesis; Oxides; Oxidation
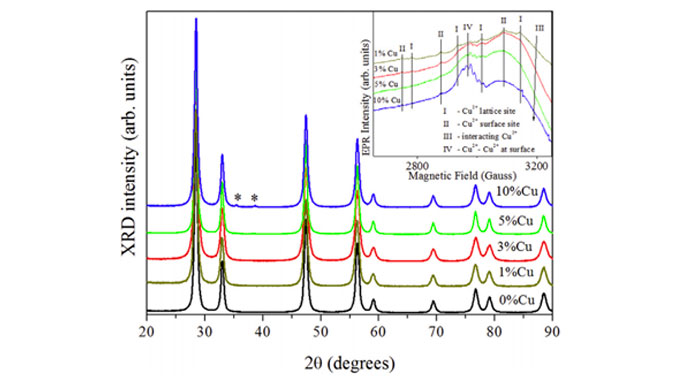
Abstract: Ceria-supported copper catalysts (Ce1xCuxO2, with x (mol) ¼ 0, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05 and 0.10) were prepared in one step through the polymeric precursor method. The textural properties of the catalysts were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld refinement, N2-physisorption (BET surface area), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), UVevisible diffuse reflectance and photoluminescence spectroscopies and temperature-programmed reduction (TPR). In a previous study ceria-supported copper catalysts were found to be efficient in the preferential oxidation of CO. In this study, we extended the catalytic application of Ce1xCuxO2 systems to n-hexane oxidation and it was verified that the catalysts were highly efficient in the proposed reaction. The best performance (up to 95% conversion) was observed for the catalysts with low copper loads (Ce0.97Cu0.03O2 and Ce0.99Cu0.01O2, respectively). The physicochemical characterizations revealed that these behaviors could be attributed to the copper species present in the catalysts and the interaction between CuO and CeO2, which vary according to the copper content.
DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.08.021