Writers: M.D. Gonçalves and Pardha S. Maram and A. Navrotsky and R. Muccillo
Keywords: Proton conductor; Barium zirconate; Powder synthesis; Impedance spectroscopy
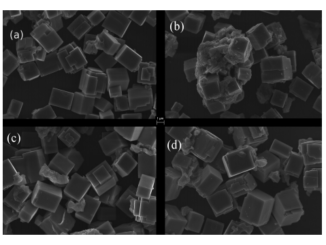
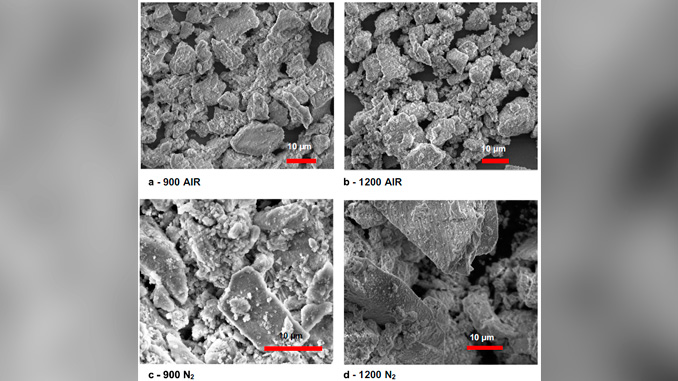
Abstract: Yttrium-doped barium zirconate ceramic powders were synthesized by the oxidant peroxide method in air and under controlled atmosphere of nitrogen inside a glove box. The powders were characterized by thermogravimetry, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. After uniaxial cold isostatic pressing, green pellets were sintered at 1600 °C for 4 h. The electrical conductivity behavior was accessed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The results show that specimens synthesized under controlled atmosphere achieved higher electrical conductivity, two orders of magnitude higher than specimens prepared in laboratory air. The enhancement in electrochemical properties and increase in sintering ability is attributed to the less carbonate contamination as a result lower grain boundary density in the samples prepared under controlled atmosphere.