Structural properties and self-activated photoluminescence emissions in hydroxyapatite with distinct particle shapes
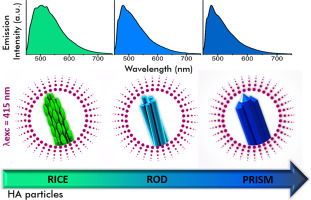
Abstract: The understanding on defect-related photoluminescence (PL) properties of hydroxyapatite (HA) particles has a fundamental importance in the technological field for the development of new non-toxic biomedical and optical devices. However, the mechanisms responsible for this intrinsic PL in HA are not completely elucidated in the literature yet. In the present paper, stoichiometric and calcium-deficient HA nano- and micro-particles were synthesized by chemical precipitation. The influence of structural and morphological features on the intrinsic PL and electronic structure of this material were investigated by varying the addition rate of the phosphate precursor (0.15, 7.00 or 600.00 mL/min) and pH (4.5–5.0 or 9.5–10.0) value adopted in the precipitation. The results indicated that the structural order at long- and short-range varied with the synthesis conditions and particle shapes (rods, needles, plates, and rices). The blue and green PL emissions were attributed to defects (bulk, surface and interface) in the samples. These defects promoted the formation of additional energy levels within the band gap, as revealed by using two distinct excitation wavelengths for photoemission measurements. The energies of these wavelengths (~ 3.54 and ~ 2.98 eV at 350 and 415 nm, respectively) were lower than the band gap energies of HA samples (from 5.59 to 5.72 eV). A general model was proposed to explain the occurrence of self-activated PL in HA structure.
Authors: Thales R. Machado, Júlio C. Sczancoski, Héctor Beltrán-Mir, Máximo S. Li, Juan Andrés, Eloisa Cordoncillo, Edson Leite & Elson Longo.
Ceramics International
Volume 44, Issue 1, January 2018, Pages 236-245
Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0272884217320916?via%3Dihub
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.164