Microwave-assisted synthesis of anatase-TiO2 nanoparticles with catalytic activity in oxygen reduction
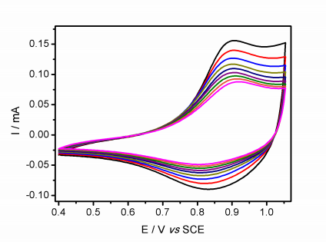
Abstract: Anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles were synthesized via fast microwave-hydrothermal route and they were characterized by BET, SEM, XRD and EIS. The synthesis process took barely 20 s, which means a low sintering time which provides a decrease in the cost and energy required in the synthesis process. Pure anatase colloidal TiO2 particles were obtained under these synthesis conditions. Particulate TiO2 films were deposited onto high porous graphite substrates and their catalytic activity toward the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline media was qualitatively demonstrated by cyclic voltammetry and linear sweep voltammetry. The ORR mechanism showed to follow the two-electron pathway via hydrogen peroxide production and further reduction to water.
Author(s): Cabello, Gema; Davoglio, Rogerio A.; Pereira, Ernesto C.
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry
Volume: 794 Pages: 36-42 Published: 2017
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.04.004