Lead-free BaBi4Ti4O15 ceramics: Effect of synthesis methods on phase formation and electrical properties
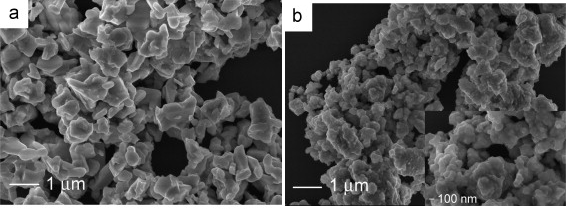
Abstract: The processing of ferroelectric BaBi4Ti4O15 (BBT) ceramics from powders prepared by conventional solid state reaction (SSR) and mechanochemical activation (MA) has been investigated. It was shown that MA synthesis reduces the synthesis temperature of BBT powders, leading to smaller particles with reduced anisotropy and consequently to smaller grain size of ceramics. Dielectric properties were investigated in a wide range of temperatures (20–800 °C) and frequencies (1.21 kHz to 1 MHz). The relative dielectric permittivity at Curie temperature was higher for solid state obtained ceramics than for the mechanically treated ones. The conductivity of sintered samples was studied, suggesting decreasing of conductivity of BBT-MA in comparison with BBT-SS ceramics. The influence of the grain and the grain boundaries contribution to the dielectric behavior in both ceramics was analyzed through impedance spectroscopy. A well-defined ferroelectric hysteresis loop was obtained for both samples.
Author(s): Bobic, J. D.; Petrovic, M. M. Vijatovic; Ilic, N. I.; et al.
Ceramics International
Volume: 41 Issue: 1 Pages: 309-316 Published: 2015
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.08.073