Influence Ca-doped SrIn2O4 powders on photoluminescence property prepared one step by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis
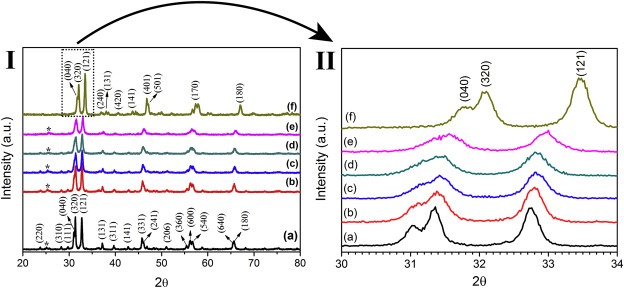
Abstract: Crystalline Ca-doped SrIn2O4 structures were prepared by a rapid and efficient Ultrasonic Pyrolysis Spray (USP) method. The Sr1-xCaxIn2O4 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 1 mol %) samples were obtained by in a single step at a temperature of 1050 °C for 1 min for the formation of particles. The powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission electron microscopy (SEM-FEG), optical diffuse reflectance and photoluminescence (PL) measurements. All diffraction peaks present in XRD patterns could be indexed to the orthorhombic structure and that with calcium percentage increments indicates the substitution of Ca2+ in the Sr2+ sites promotes a decrease in its lattice parameters of the structure. MEV-FEG images show that the Sr1-xCaxIn2O4 particles have a spherical predominance, with a porous surface in the form of foam for x = 0 and a surface with low roughness and low porosity with an increase in the percentage of Ca2+ ion, especially for the 1 mol % of Ca2+. The gap energy varied between 4.56 eV and 4.86 eV, being influenced by the structural modifications motivated by increase of Ca2+ ion contained in the SrIn2O4 matrix. The PL emission spectrum of the samples presents a broad band behavior with emission intensity predominant in the blue-green region, having the sample with x = 0.1 the highest PL intensity. The chromaticity coordinates were calculated for the sample based on the PL spectrum and coordinates x and y show that the samples have blue emission. Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis was an effective technique for Ca-doped SrInO4 powder production using short production times with hold great potential for photoluminescent emitters.
Author(s): Medeiros, P. N.; Santiago, A. A. G.; Ferreira, E. A. C.; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds
Volume: 747 Pages: 1078-1087 Published: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.090




