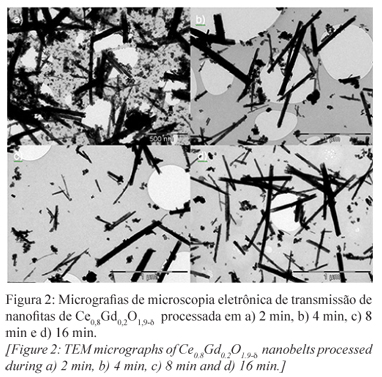
Study of growth of gadolinium-doped ceria nanobelts by a hydrothermal microwave system
Abstract: Cerium oxide (ceria) has attracted attention because of its important applications such as solid oxide fuel cells, catalysts for automobile exhaust gas, catalysts to obtain hydrogen, UV blockers, biomaterials, etc.. Control methods for synthesis of ceria are of great importance to explain or predict these properties. Thus, the objective of this work was to study the growth of cerium oxide nanobelts in a microwave-assisted hydrothermal system, where in 8 min 330 nm nanobelts were obtained at 130 ºC and 3 atm. The results collaborate to the research on reformers for ethanol and/or solid oxide fuel cells anode.
Author(s): Souza, J. A.; Criado, D.; Zuniga, A.; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics
Volume: 114 Issue: 17 Published: 2013
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S0366-69132013000300012
PDF: Study of growth of gadolinium-doped ceria nanobelts by a hydrothermal microwave system