Characterization of hard coatings produced by laser cladding using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy technique
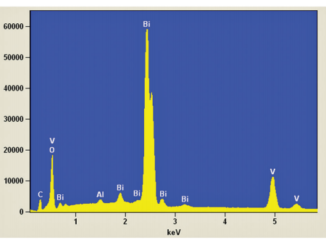
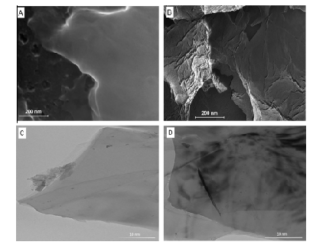
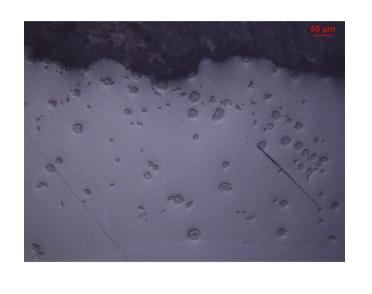
Abstract: Protective coatings with a high abrasive wear resistance can be obtained from powders by laser cladding technique, in order to extend the service life of some industrial components. In this work, laser clad layers of self-fluxing NiCrBSi alloy powder mixed with WC powder have been produced on stainless steel substrates of austenitic type (AISI 304) in a first step and then chemically characterized by laserinduced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technique. With the suitable laser processing parameters (mainly output power, beam scan speed and flow rate) and powders mixture proportions between WC ceramics and NiCrBSi alloys, dense pore free layers have been obtained on single tracks and on large areas with overlapped tracks. The results achieved by LIBS technique and applied for the first time to the analysis of laser dads provided the chemical composition of the tungsten carbides in metal alloy matrix. Different measurement modes (multiple point analyses, depth profiles and chemical maps) have been employed, demonstrating the usefulness of LIBS technique for the characterization of laser dads based on hardfacing alloys. The behavior of hardness can be explained by LIBS maps which evidenced the partial dilution of some WC spheres in the coating. (C) 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Varela, JA; Amado, JM; Tobar, MJ; Mateo, MP; Yanez, A; Nicolas, G
APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE
Volume: 336 Pages: 396-400 Published: MAY 1 2015
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.037