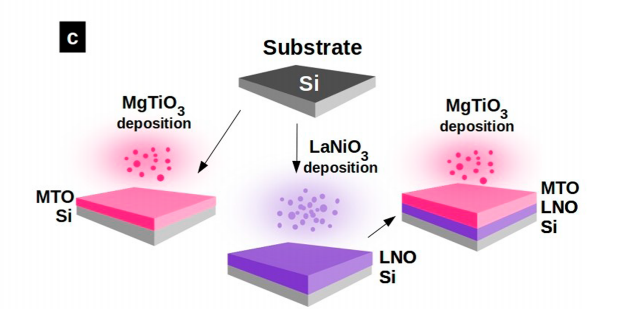
Controlling the Electronic, Structural, and Optical Properties of Novel MgTiO3/LaNiO3 Nanostructured Films for Enhanced Optoelectronic Devices
Abstract: This study systematically investigated the electronic, structural, and optical properties of MgTiO3 (MTO), LaNiO3 (LNO), and MgTiO3/LaNiO3 (MTO/LNO) nanostructured films grown on Si(100) substrates by the pulsed laser deposition method. The structural characterizations obtained by X-ray diffraction revealed a preferred (003) orientation for the MTO film, while the LNO film was polycrystalline. The diffraction peaks corresponded to a rhombohedral structure, which was confirmed by micro-Raman spectroscopy for both nanostructured films. The MTO/LNO heterostructure was polycrystalline and exhibited the diffraction peaks of both the MTO and the LNO phases. Additionally, the results revealed that the LNO films did not have a significant photoluminescence (PL) emission, while an intense broad infrared luminescence centered at 724 nm appeared for the MTO nanostructured film. Surprisingly, for the MTO/LNO heterostructure, the PL emission profile exhibited a dual-color emission with an intense broad luminescence in the blue region (maximum centered at 454 nm) and an intense near-infrared emission (maximum centered at 754 nm), respectively, mainly because of the effect of interface defects, which induced a significant change in the PL behavior. Therefore, our experimental results correlated with the theoretical simulations based on the periodic density functional theory formalism and contributed to a deeper understanding of the charge/energy transfer processes occurring in the MTO/LNO/Si interfaces, and toward the exploitation of the close relationship between the structure and properties of these new functional materials.
Author(s): Mazzo, TM; Macario, LR; Gorup, LF; Bouquet, V; Deputier, S; Ollivier, S; Guilloux-Viry, M; Albuquerque, AR; Sambrano, JR; La Porta, FA
ACS APPLIED NANO MATERIALS
Volume: 2 Pages: 2612-2620 Published: MAY 2019
DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.8b02110