A novel synthesis route to obtain magnetic nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite with photo-Fenton activity
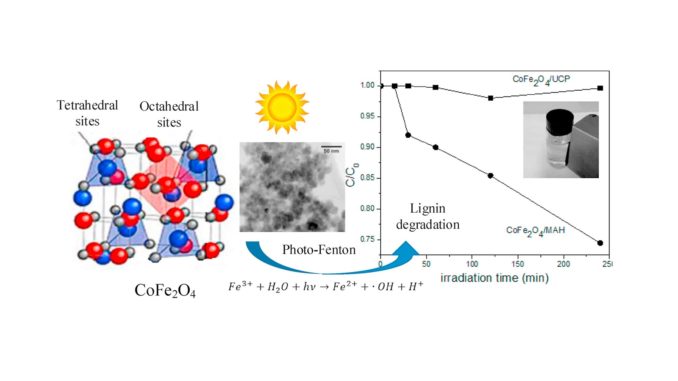
Abstract: A novel unconventional coprecipitation procedure (UCP) followed by a simple and fast microwave-assisted hydrothermal (MAH) treatment was used to synthesize a new nanocrystalline magnetic cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4/MAH) with photo-Fenton activity. The Co-ferrite nanoparticles were obtained at room temperature in the absence of surfactants and their photo-Fenton activity was evaluated through lignin degradation. It was found that microwave hydrothermal treatment is mandatory to obtain magnetic and photoactive Co-ferrite. According to XRD Rietveld refinements and FTIR, the photoactivity was mainly attributed to the Co2+ cation migration from octahedral to tetrahedral sites in the ferrite structure during the MAH treatment, leading, consequently, to a higher Fe3+ incorporation at octahedral sites, which strongly participate in the photo-Fenton degradation mechanism. The magnetic property of the CoFe2O4/MAH ferrite nanoparticles was confirmed by magnetometry and provided an easy catalyst separation.
Author(s): Souza, B.G.; Figueira, G.; Carvalho, M.H.; Alcaraz-Gonzalez, V.; Saldaña-Flores, K.E.; Godinho Jr., M.; Oliveira, A.J.A.; Kiminami, R.H.G.A.; Ruotolo, L.A.M.; Urquieta-González, E.A.
Materials Chemistry and Physics
Published: 1 January 2021, Volume 257, 123741
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123741
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).




