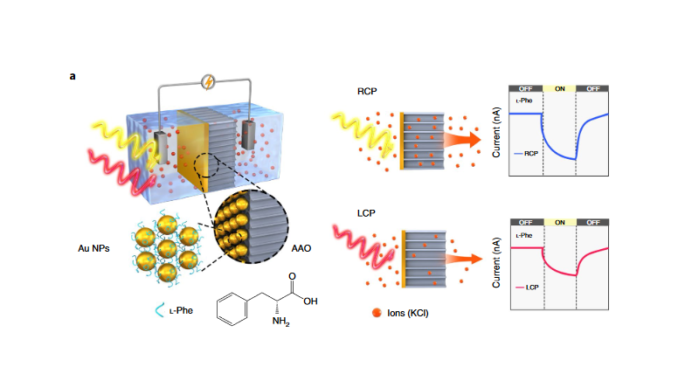
Polarization-sensitive optoionic membranes from chiral plasmonic nanoparticles
Abstract: Optoelectronic effects differentiating absorption of right and left circularly polarized photons in thin films of chiral materials are typically prohibitively small for their direct photocurrent observation. Chiral metasurfaces increase the electronic sensitivity to circular polarization, but their out-of-plane architecture entails manufacturing and performance trade-offs. Here, we show that nanoporous thin films of chiral nanoparticles enable high sensitivity to circular polarization due to light-induced polarization-dependent ion accumulation at nanoparticle interfaces. Self-assembled multilayers of gold nanoparticles modified with l-phenylalanine generate a photocurrent under right-handed circularly polarized light as high as 2.41 times higher than under left-handed circularly polarized light. The strong plasmonic coupling between the multiple nanoparticles producing planar chiroplasmonic modes facilitates the ejection of electrons, whose entrapment at the membrane–electrolyte interface is promoted by a thick layer of enantiopure phenylalanine. Demonstrated detection of light ellipticity with equal sensitivity at all incident angles mimics phenomenological aspects of polarization vision in marine animals. The simplicity of self-assembly and sensitivity of polarization detection found in optoionic membranes opens the door to a family of miniaturized fluidic devices for chiral photonics.
Author(s): Cai, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Hao, C.; Ma, W.; Sun, M.; Wu, X.; Qin, X.; Colombari, F.M.; Moura, A.F.; Xu, J.; Silva, M.C.; Carneiro-Neto, E.B.; Gomes, W.R.; Vallée, R.A. L. ; Pereira, E.C.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Klajn, R.; Kotov, N.A. ; Kuang, H.
Nat. Nanotechnol.
Published: 14 March 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01079-3
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).