Revisiting the hydroxylation phenomenon of SiO2: a study through “hard-hard” and “soft–soft” interactions
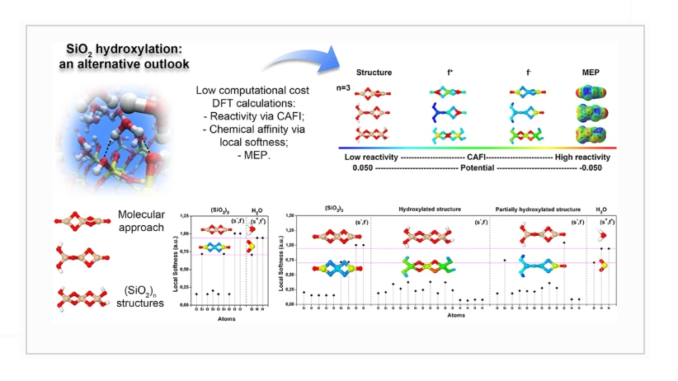
Abstract: Surface hydroxylation has been extensively studied over the years for a variety of applications, and studies involving hydroxylation of different silica surfaces are still carried out due to the interesting properties obtained from those modified surfaces. Although a number of theoretical studies have been employed to evaluate details on the hydroxylation phenomenon on silica (SiO2) surfaces, most of these studies are based on computationally expensive models commonly based on extended systems. In order to circumvent such an aspect, here we present a low-cost theoretical study on the SiO2 hydroxylation process aiming to evaluate aspects associated with water-SiO2 interaction. Details about local reactivity, chemical softness, and electrostatic potential were evaluated for SiO2 model substrates in the framework of the density functional theory (DFT) using a molecular approach. The obtained results from this new and promising approach were validated and complemented by fully atomistic reactive molecular dynamics (FARMD) simulations. Furthermore, the implemented approach proves to be a powerful tool that is not restricted to the study of hydroxylation, opening a promising route for low computational cost to analyze passivation and anchoring processes on a variety of oxide surfaces.
Author(s): Gomes, O. P.; Rheinheimer, J. P. C.; Dias, L. F. G.; Batagin-Neto, A.; Lisboa, P. N.
Journal of Molecular Modeling
Published: 07 April 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05107-w
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).