Effect of calcination temperature and pressure-assisted heat treatment on the dye degradation performance of SnO2 photocatalyst obtained by a simple synthesis method
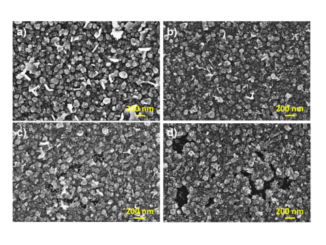
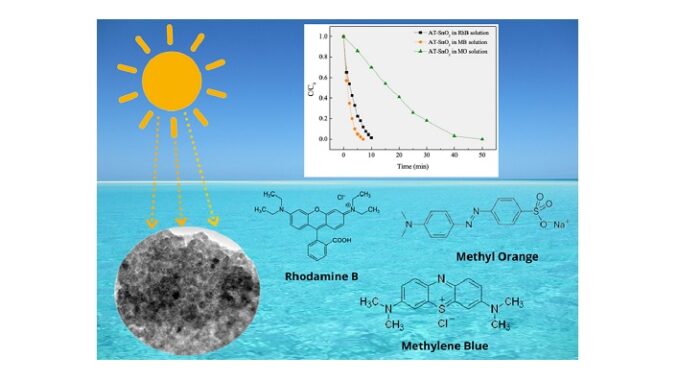
Abstract: SnO2 particles were synthesized by the co-precipitation method. The effect of annealing temperature and pressure-assisted heat treatment (PAHT) on their structural, morphological and optical properties were investigated. Moreover, the synthetized SnO2 at ambient temperature and annealed at 400 and 700 °C as well as the particles submitted at the PAHT were efficient for the photocatalytic degradation of the Rhodamine B (RhB) dye solution under UV irradiation, showing a degradation efficiency above 99% for all samples studied. However, the SnO2 sample obtained at ambient temperature (AT-SnO2) exhibited complete RhB photodegradation in only 10 min. This surprising performance of the AT-SnO2 sample led to the investigation of its performance for the degradation of two other dyes, methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO), and the results also revealed complete degradation of these dyes. These findings were superior to those found in the literature for SnO2 samples synthesized by different methods.
Author(s): da Trindade, L. G.; Rocha, A. C. B.; Teodoro, V.; da Silva, V. T.; Trench, A. B.; Cordoncillo, E.; Teodoro, M. D.; Tebcherani, S. M.; Longo, E.; Mazzo, T. M.
Materials Research Bulletin
Published: September 2022, Volume 153, 111914
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.111914
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).