Manganese Defective Clustering: Influence on the Spectroscopic Features of Ceria-Based Nanomaterials
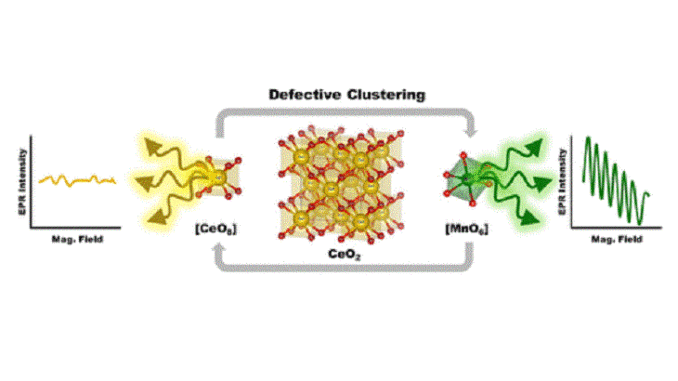
Abstract: The influence of manganese modification on the spectroscopic features of manganese-doped CeO2 systems synthesized by the microwave-assisted hydrothermal route and their correlation with the presence of O defective structures were verified, focusing on their interaction with poisonous atmospheres. Raman and electron paramagnetic resonance studies confirmed the presence of defective clusters formed by dipoles and/or quadrupoles. The number of paramagnetic species was found to be inversely proportional to the doping concentration, resulting in an increase in the Mn2+ signal, likely due to the reduction of Mn3+ species after the interaction with CO. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy data showed the pure system with 33% of its cerium species in the Ce3+ configuration, with an abrupt decrease to 19%, after the first modification with Mn, suggesting that 14% of the Ce3+ species are donating one electron to the Mn2+ ions, thus becoming nonparamagnetic Ce4+ species. On the contrary, 58% of the manganese species remain in the Mn2+ configuration with five unpaired electrons, corroborating the paramagnetic feature of the samples seen in the electron paramagnetic resonance study.
Author(s): D. C. Amaral; L. S. R. Rocha; L. I. Granone; M. M. Lage; M. S. Churio; M. D. Sanchez; E. Longo; H. M. S. Nascimento; M. Assis; F. Moura; M. A. Ponce
Inorg. Chem.
Published: July 21, 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c01597
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).




