Insights into the role of surface properties on the optical, electronic and nanoparticles morphology of scheelite BaMoO4
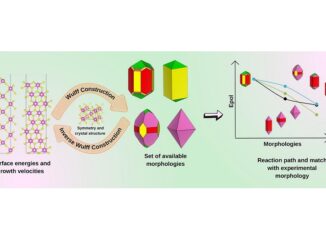
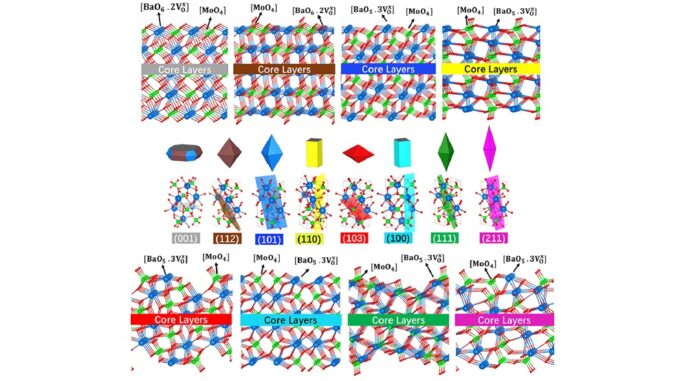
Abstract: Wide band gap semiconductors, such as barium molybdate (BaMoO4), remain to attract much interest due to their excellent optical, catalytic, and electronic applications. Herein, computational simulations based on the density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out to conduct a systematic study of the electronic, structural, and catalytic properties of BaMoO4 bulk and its (001), (112), (101), (110), (103), (100), (111) and (211) surfaces. It was found that the relative stability order (001) > (112) > (101) > (110) > (103) > (100) > (111) > (211). Band gap energies between 2.06 eV (211) and 4.56 eV (101) were observed. The (112) and (103) surfaces are p-type, while the others exhibit characteristics of n-type semiconductors. Additionally, by the band edge alignment analysis, all surfaces are suitable for promoting the O2 to O2- and the H+ to H2 reactions. Finally, a detailed mapping of morphological transformation routes of nano/microstructures was built, contributing experimentalists to frontier research with scheelite-type materials. Therefore, understanding and controlling the morphology allows the development of new materials with highly customized properties and functionality, leading to advances in various fields such as electronics, energy storage and catalysis, among other applications.
Author(s): José A.S. Laranjeira, Sergio A. Azevedo, Nicolas F. Martins, Felipe A. La Porta, Elson Longo, Julio R. Sambrano
Surfaces and Interfaces
Available online 26 January 2024, 103894
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2024.103894
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).