Fast and efficient processes for oxidation and monitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental matrices
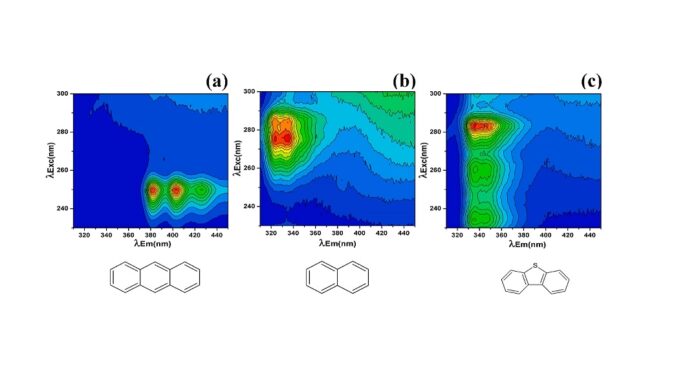
Abstract: This study proposes a new approach for the efficient photodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and derivatives. PAH removal was achieved in just a few minutes using a microwave photochemical reactor capable of producing a high concentration of •OH (2.3 mmol L−1 h−1). Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy coupled to parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) was used for quantifying two PAH and one alkylated PAH at low concentrations (μg L−1). These results highlight the high potential of the photochemical degradation system coupled to EEM-PARAFAC as an alternative fast, inexpensive, and efficient approach for environmental remediation studies of PAH.
Author(s): Kelvin C. Araújo, Eryka T.D. Nóbrega, Ailton J. Moreira, Sherlan G. Lemos, Wallace D. Fragoso, Ernesto C. Pereira
Catalysis Communications
Available online 28 December 2023, 106834
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2023.106834
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).




