Carbon Nitrides in Photoelectrochemistry: State of the Art and Perspectives Beyond Water Splitting
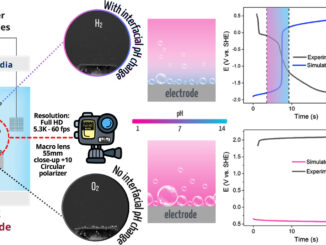
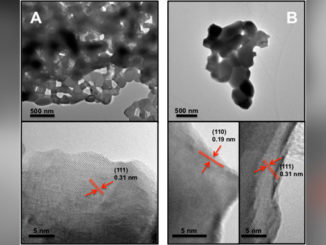
Abstract: Photoelectrodes made from cost-effective materials are the most desired for practical photoelectrochemical (PEC) applications, aiming to help in the imminent environmental crisis that urges an energetic transition. A prominent class of semiconductors are the polymeric carbon nitrides (PCN), which appear to be an eco-friendly solution particularly for green hydrogen production through water splitting, value-added organic compounds obtention from biomass upgrading, or CO2 reduction; even green ammonia can be obtained by PEC reduction of N2. In this sense, monitoring dangerous environmental species or converting them into less toxic ones can also be performed through PEC using carbon nitride-based electrodes. In this review, we provide an overview of the basics of PCN applications in PEC, including commonly employed strategies to enhance their performance. Additionally, we discuss the current state-of-the-art for PCN in PEC water splitting as well as lesser-explored areas such as biomass upgrading, environmental remediation, photoelectroanalytical sensing, and light-driven CO2 and N2 reduction reactions. Finally, we present an overview of prospects for PCN material in PEC.
Author(s): Sirlon F. Blaskievicz, Juliana Lucca Francisco, Frank Marken, and Lucia Helena Mascaro
ACS Appl. Energy Mater.
Publushed: March 26, 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.3c02623
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).