Structure, morphology and photoluminescence emissions of ZnMoO4: RE (3+) = Tb3+ – Tm3+ – X Eu3+ (x=1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 mol%) particles obtained by the sonochemical method
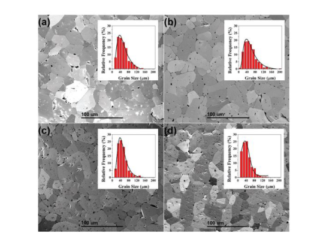
Abstract: ZnMoO4 and ZnMoO4: RE3+ 1% Tb3+, 1% Tm3+, x Eu3+ (x=1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 mol%) particles were prepared by a sonochemical method. The influence of the dopant content on photoluminescent behavior was investigated. The X-ray diffraction results confirmed the formation of the alpha-ZnMoO4 phase with a triclinic crystalline structure. The influence of the chemical compositions on photoluminescence emissions has been studied and the results clearly show the specific emissions of Tb3+ and Eu3+, simultaneously, with a strong contribution of the matrix. Band gap values are in the range of 3.55-4.25 eV. From the values calculated for the CIE coordinates, it was observed that this material develops an emission tendency in the orange-red region. It has been demonstrated for the first time that the sample ZnMoO4: 1% Tb3+, 1% Tm3+, 2% molEu(3+), presented higher photoluminescence intensity. At higher concentrations of RE3+, the quenching effect was observed. The morphology of samples are interpreted based on a comparative analysis of the calculated and experimental field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images. First-principle calculations at a density functional theory level were performed to obtain the values of surface energies and relative stability of the (120), (001), (011), (201), and (100) surfaces by employing the Wulff construction. A complete map of the available morphologies of ZnMoO4 and ZnMoO4:12.5%molEu(3+) is obtained and a possible explanation for the transformation processes is provided in which the experimental and theoretical morphologies can match. The present study offers a fundamental knowledge that is expected to enable the fabrication of ZnMoO4-based phosphor materials with a controllable emission peak shift and intensity. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Lovisa, LX; Oliveira, MC; Andres, J; Gracia, L; Li, MS; Longo, E; Tranquilin, RL; Paskocimas, CA; Bomio, MRD; Motta, FV
JOURNAL OF ALLOYS AND COMPOUNDS
Volume: 750 Pages: 55-70 Published: JUN 25 2018
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.394