Photoluminescence emission in zirconium-doped calcium copper titanate powders
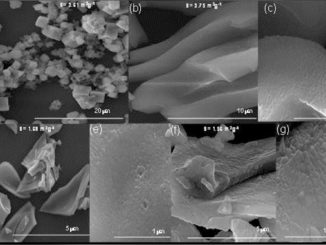
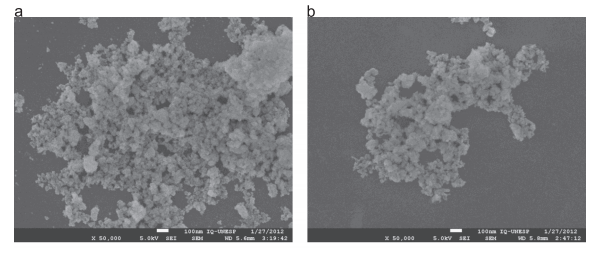
Abstract: Intense photoluminescence (PL) emission was observed in Zr-doped calcium copper titanate powders. The compounds were synthesized by a soft chemical method and heat treated at temperatures between 300 and 850 degrees C. The decomposition of the precursors was examined by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared, Fourier transform Raman, and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopies; as well as PL analysis. Here, we discuss the role of the structural ordering, which facilitates the self-trapping of electrons and charge transfer, and review the mechanism that triggers the PL. The most intense PL emission was obtained for the sample with 5% Zr calcined at 750 degrees C, which is neither highly disordered nor completely ordered at similar to 520 nm. (C) 2015 Elsevier Ltd and Techna Group S.r.l. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Moura, F; Cabral, AC; Rocha, LSR; Aguiar, EC; Simoes, AZ; Longo, E
CERAMICS INTERNATIONAL
Volume: 42 Pages: 4837-4844 Published: MAR 2016
PDF: Photoluminescence emission in zirconium-doped calcium copper titanate powders
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.169