Titanium dioxide nanotubes addition to self-adhesive resin cement: Effect on physical and biological properties
Objectives. This study has investigated the influence of Titanium dioxide nanotubes (TiO2-nt) addition to self-adhesive resin cement on the degree of conversion, water sorption, and water solubility, mechanical and biological properties.
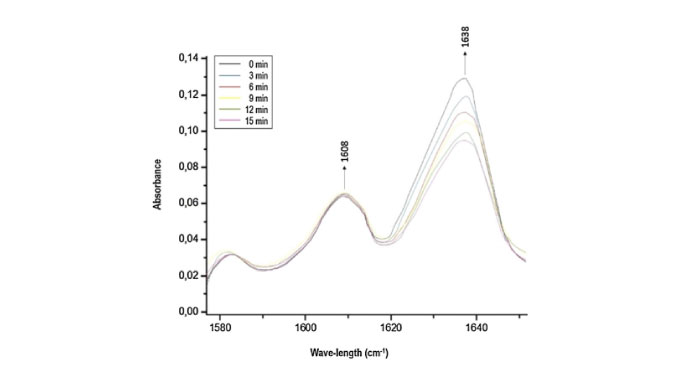
Methods. A commercially available auto-adhesive resin cement (RelyX U200(TM), 3M ESPE) was reinforced with varying amounts of nanotubes (0.3, 0.6, 0.9 wt%) and evaluated at different curing modes (self- and dual cure). The DC in different times (3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 min), water sorption (Ws) and solubility (Sl), 3-point flexural strength (sf), elastic modulus (E), Knoop microhardness (H) and viability of NIH/3T3 fibroblasts were performed to characterize the resin cement.
Results. Reinforced self-adhesive resin cement, regardless of concentration, increased the DC for the self- and dual-curing modes at all times studied. The concentration of the TiO2-nt and the curing mode did not influence the Ws and Sl. Regarding sf, concentrations of both 0.3 and 0.9 wt% for self-curing mode resulted in data similar to that of dual-curing unreinforced cement. The E increased with the addition of 0.9 wt% for self-cure mode and H increased with 0.6 and 0.9 wt% for both curing modes. Cytotoxicity assays revealed that reinforced cements were biocompatible.
Significance. TiO2-nt reinforced self-adhesive resin cement are promising materials for use in indirect dental restorations. Taken together, self-adhesive resin cement reinforced with TiO2-nt exhibited physicochemical and mechanical properties superior to those of unreinforced cements, without compromising their cellular viability.
Author(s): Ramos-Tonello, CM (Ramos-Tonello, Carla M.); Lisboa, PN (Lisboa-Filho, Paulo N.); Arruda, LB (Arruda, Larisa B.); Tokuhara, CK (Tokuhara, Cintia K.); Oliveira, RC (Oliveira, Rodrigo C.); Furuse, AY (Furuse, Adilson Y.); Rubo, JH (Rubo, Jose H.); Borges, AFS (Borges, Ana Flavia S.)
DENTAL MATERIALS
Volume: 33 | Ed: 7 | Pages: 866-875 | Published: JUL 2017
DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2017.04.022