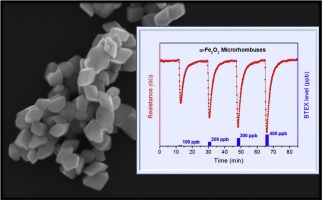
BTEX gas sensor based on hematite microrhombuses
Abstract: Over the past fifty years, gas sensors based on metal semiconducting oxides (MOXs) have drawn attention due to their performance in detecting various gases. Thus, we report herein on a BTEX gases sensor based on hematite (α-Fe2O3) microrhombuses synthesized via the hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy analyses indicated the presence of a pristine hematite phase after hydrothermal treatment. Electron microscopy analyses revealed that the hematite sample consists of single-crystals with a rhombus-like shape and an average size of 140 nm. Electrical measurements pointed out that hematite microrhombuses were sensitive towards sub-ppm BTEX levels, in which the minimum detected level was 3 ppb and the long-term stability was 1 month. The results presented here demonstrate the potential of hematite microrhombuses as a sensing material to manufacture BTEX gas sensor devices.
Author(s): Luís F. da Silva, Ariadne C. Catto, Sandrine Bernardini, Tomas Fiorido, João V. N. de Palma, Waldir Avansi Jr, Khalifa Aguir, Marc Bendahan.
Sensors and Actuators B
Chemical 326 (2021) 128817