Evaluation and characterization of edible carboxymethylcellulose biofilm containing chitosan nanoparticles and turmeric
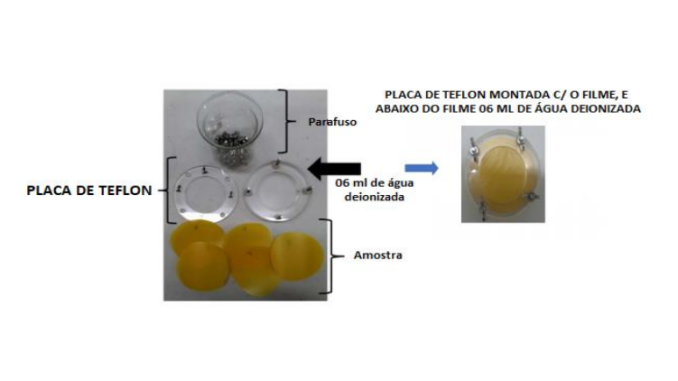
Abstract: The production of biofilms and polymeric coatings based on natural polymers in order to apply them as food packaging is constantly being researched due to the need to decrease the volume of discarded plastic packaging and optimize the properties and validity of food. Among the immense variety of polymers used for this purpose, carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) has stood out for presenting favorable characteristics for the filmogenic solutions formation, besides being biodegradable and presenting low cost. Aiming to enhance the natural properties of this polymer, researchers have used additives that are incorporated into the filmogenic solution such as chitosan nanoparticles (NSQ) and turmeric. Chitosan is also a natural polymer, widely used in applications in the fields of pharmacology, biomaterials technology, biomedicine, agriculture and the cosmetics and food industries. Turmeric derived from saffron, has antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, which has aroused a lot of interest, especially in the food industry, aiming to replace synthetic antioxidants with these natural materials. In this work, chitosan nanoparticles were prepared by ionotropic gelation and incorporated into the polymer (CMC), along with turmeric, in order to reinforce and enhance the natural properties of this polymer for the preparation of edible biofilms. After preparation, they are characterized by analysis of mechanical properties, water vapor permeability and contact angle.
Author(s): Santos, V. S.; dos Santos, V. S.; Fernandes, R. D.; Ferreira, C. R.; Aouada, F. A.; Americo-Pinheiro, J. H. P.; de Moura, M. R.
Revista Matéria
Published: 2021
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-707620210001.1226
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).