Chiral phonons in microcrystals and nanofibrils of biomolecules
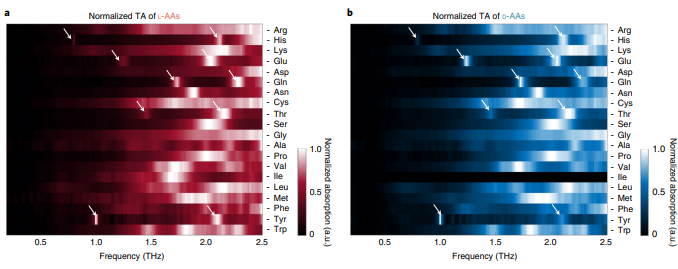
Abstract: Chiral phonons are concerted mirror-symmetric movements of atomic groups connected by covalent and intermolecular bonds. Such lattice vibrations in crystals of biomolecules should be highly specific to their short- and long-range organizations, but their chiroptical signatures and structure–property relationships remain uncertain. Here we show that terahertz chiroptical spectroscopy enables the registration and attribution of chiral phonons for microscale and nanoscale crystals of amino acids and peptides. Theoretical analysis and computer simulations indicate that sharp mirror-symmetric bands observed for left- and right-handed enantiomers originate from the collective vibrations of biomolecules interconnected by hydrogen bonds into helical chains. The sensitivity of chiral phonons to minute structural changes can be used to identify physical and chemical differences in seemingly identical formulations of dipeptides used in health supplements. The generality of these findings is demonstrated by chiral phonons observed for amyloid nanofibrils of insulin. Their spectral signatures and polarization rotation strongly depend on their maturation stage, which opens a new door for medical applications of terahertz photonics.
Author(s): Choi, W.J.; Yano, K.; Cha, M.; Colombari, F.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Sun, K.; Kruger, J.M.; Moura, A.F.; Kotov, N.A.
Nat. Photon.
Published: 21 March 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-022-00969-1
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).