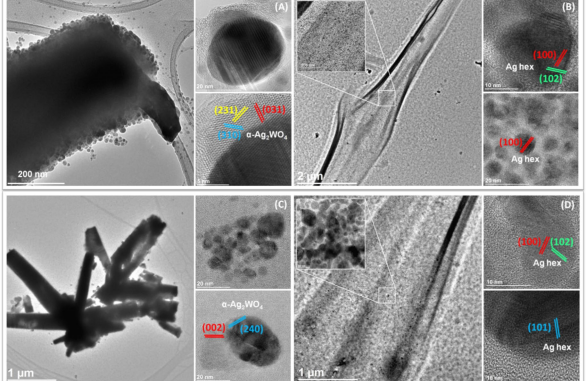
Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by a chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 composite generated by femtosecond laser irradiation
Abstract: In the current COVID-19 pandemic, the next generation of innovative materials with enhanced anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity is urgently needed to prevent the spread of this virus within the community. Herein, we report the synthesis of chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 composites synthetized by femtosecond laser irradiation. The antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Methicilin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), and Candida albicans was determined by estimating the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal/fungicidal concentration (MBC/MFC). To assess the biocompatibility of chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 composites in a range involving MIC and MBC/MFC on keratinocytes cells (NOK-si), an alamarBlue™ assay and an MTT assay were carried out. The SARS-CoV-2 virucidal effects was analyzed in Vero E6 cells through viral titer quantified in cell culture supernatant by PFU/mL assay. Our results showed a very similar antimicrobial activity of chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 3.3 and 6.6, with the last one demonstrating a slightly better action against MSSA. The chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 9.9 showed a wide range of antimicrobial activity (0.49–31.25 µg/mL). The cytotoxicity outcomes by alamarBlue™ revealed that the concentrations of interest (MIC and MBC/MFC) were considered non-cytotoxic to all composites after 72 h of exposure. The Chitosan/α-Ag2WO4 (CS6.6/α-Ag2WO4) composite reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral titer quantification up to 80% of the controls. Then, our results suggest that these composites are highly efficient materials to kill bacteria (Escherichia coli, Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, and the yeast strain Candida albicans), in addition to inactivating SARS-CoV-2 by contact, through ROS production.
Author(s): Pereira, P.F.S.; Paula e Silva, A.C.A.; Pimentel, B.N.A.S.; Pinatti, I.M.; Simões, A.Z.; Vergani, C.E.; Barreto-Vieira, D.F.; Silva, M.A.N.; Miranda, M.D.; Monteiro, M.E.S.; Tucci, A.; Doñate-Buendía, C.; Mínguez-Vega, G.; Andrés, J.; Longo, E.
Scientific Reports
Published: 17 May 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11902-5
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).