Photoactivity of boron-or nitrogen-modified TiO2 for organic pollutants degradation: Unveiling the photocatalytic mechanisms and by-products
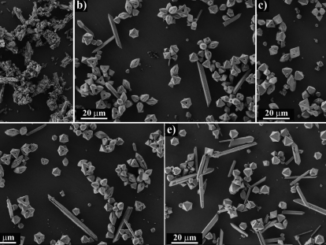
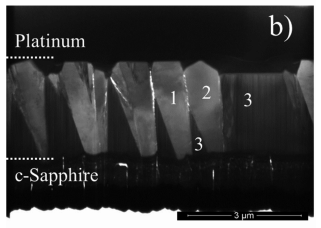
Abstract: The degradation of fluoxetine (FLX) emerging pollutant and the formation of by-products, potentially present in environmental ecosystems, was investigated from photocatalytic processes. Applying different synthesis methods, nitrogen (TiN) or boron (TiB)-modified TiO2 presented oxygen vacancies (Vö) responsible for generating intermediate energy levels, which acted as shallow traps to minimize the recombination processes and maintain the efficient separation of charge carriers. All photocatalysts showed the potential to produce hydroxyl radicals (•OH) from the oxidation of water in h+(VB), achieving 100% of RhB degradation under UV or visible irradiation. For the degradation of FLX, an alternative mechanism mediated by one of the by-products was confirmed after LC-MS-Q-TOF analysis. The protonation, dehalogenation and hydroxylation steps of FLX (m/z[H+] =310.1419) produce the transformation products TP8 (m/z[H+] = 310.1430), TP6 (m/z[H+] = 286.1454), and TP9 (m/z = 161.0221 (-ESI)), respectively. Other by-products have been identified after photodegradation, and their presence in FLX-contaminated ecosystems cannot be ignored. Therefore, high-performance photocatalysts obtained in this study are real alternatives for the environmental remediation of organic pollutants in aquatic ecosystems.
Author(s): Moreira, A.J.; dos Santos, B.R.M.; Dias, J.A.; Rabello, P.T.; Coelho, D.; Mascaro, L.H.; Freschi, G.P.G.; Gobato, Y.G.; Galeti, H.V.A.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Pereira, E.C.
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering
Published: February 2023, Volume 11, Issue 1, 109207
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.109207
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).