Unveiling photoluminescent response of Ce-doped CaCu3Ti4O12: An experimental-theoretical approach
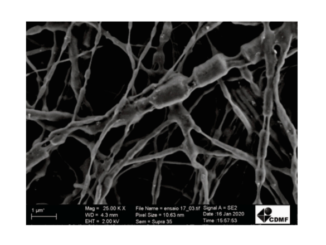
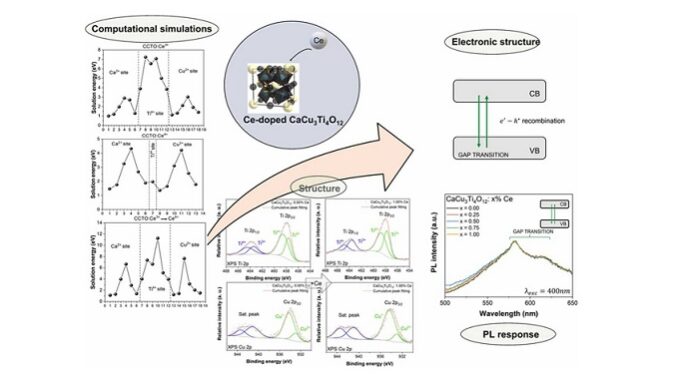
Abstract: CaCu3Ti4O12: x% Ce (x = 0.00, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.00) ceramic composites were prepared via solid-state reaction. Theoretical atomistic simulations were combined with experimental techniques to uncover Ce effects in the (micro)structure and photoluminescence of CaCu3Ti4O12-based ceramics. Application of perovskites ceramics in optoelectronics have been limited by their specific, narrow emission range, which compromise operational efficiency, pushing for the development of novel perovskite-emissive materials. This study results confirm that Ce ions are incorporated at Ca sites within the CaCu3Ti4O12 lattice, inducing point metal and oxygen vacancies in the optical bandgap region. Shallow-level defects (VCa/VO) were associated with broadband violet-blue photoluminescent (PL) emissions. Better color rendering may be a direct consequence of crystalline field splitting/wider PL emission. Furthermore, results demonstrate that PL on CaCu3Ti4O12: Ce system intensity can be modulated by structural defects, making it promising for applications in optoelectronics.
Author(s): Moreno, H.; Damm, M.; Freitas, S. M.; Rezende, M. V. S.; Simoes, A. Z.; Biasotto, G.; Mastelaro, V. R.; Teixeira, V. C.; Ramirez, M. A.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds
Published: 25 November 2022, Volume 923, 166185
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166185
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).