Graphite nanosheet/polyaniline nanocomposites: Effect of in situ polymerization and dopants on the microstructure, thermal, and electrical conduction properties
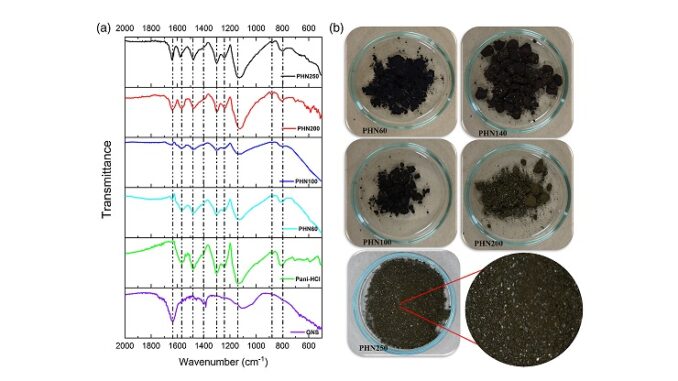
Abstract: This work proposed a study of in situ polymerization of polyaniline (Pani) in the presence of graphite nanosheets (GNS). The study focused on the different physical–chemical interactions promoted among them during the Pani synthesis using different dopants (HCl and DBSA). By means of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetry (TG/DTG), and DC electrical conductivity, the study demonstrated the production of nanocomposites with different electrical, thermal, and morphological properties and correlating them with the different physicochemical interactions evidenced from the different dopants used. The type of anchoring has been shown to directly influence the amount of GNS that could be incorporated into the reaction medium. It also demonstrated as highlight the possible existence of a hybrid intercalation/pseudo-intercalation process that was responsible for promoting an increase of up to 50°C in the thermal stability of the nanocomposites depending on the general characteristics of the synthesized Pani type. The electrical conductivity of the nanocomposites proved to be dependent on the type of dopant, the GNS/Pani interaction, and the regularity of the Pani coating on the nanostructure surface, resulting in a non-universal percolation profile.
Author(s): Martin, E. S.; Sanches, A. O.; Maraschin, T. G.; de Souza Basso, N. R.; de Paula, F. R.; Malmonge, J. A.
Journal of Applied Polymer Science
Published: 18 March 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/app.52363
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).