Writers: Mamani, NC; da Silva, RT; de Zevallos, AO; Cotta, AAC; Macedo, WAD; Li, MS; Bernardi, MIB; Doriguetto, AC; de Carvalho, HB
Keywords: Dilute magnetic oxides; Defect ferromagnetism; Co-doped ZnO thin films; Structural and magnetic characterization; diluted magnetic semiconductors; electronic-structure; giant magnetoresistance; raman-scattering; zinc-oxide; defects; clusters; exchange; transport; anatase
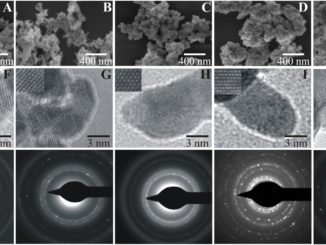
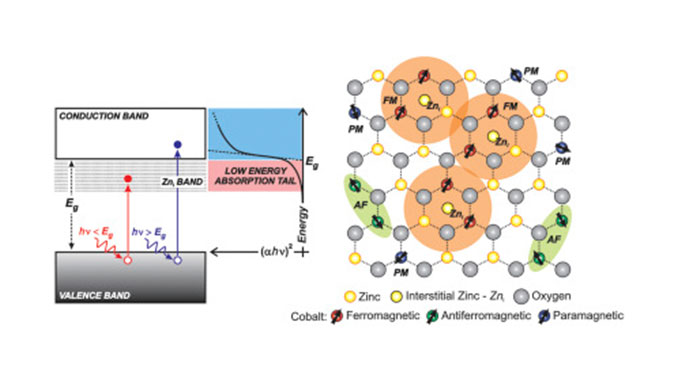
Abstract: The complete comprehension of the magnetic properties of the dilute magnetic oxides has emerged as one of the major challenges in the fields of materials science and condensed matter physics. Up to now, there is no consensus about the mechanism behind the so often observed room temperature ferromagnetism. However it is well known that defects plays an important role in the context. Here we present the study of the correlation between the structural and the magnetic properties of nanoparticulate Co-doped ZnO (Zn1-xCoxO, x = 0.02 and 0.08) thin films prepared via Electron Beam-Physical Vapor Deposition. The structural results confirms the incorporation of the Co2+ ions into the ZnO host matrix with no secondary phases. Magnetic measurements show a robust ferromagnetic order for the thin film with x = 0.08, whereas for the sample with x = 0.02 only a tiny ferromagnetism were observed. We could explain the differences in the magnetic behavior entirely under the scope of the spin-split impurity band model. In this work we also present convincing evidences of the no correlation between the oxygen vacancies and the desired room temperature ferromagnetism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.183