Writers: Ana C. de O. Gomes, Beatriz Uieda, Andre A. Tamashiro, Adhemar C. Ruvolo Filho, Luiz A. Pessan, Caio M. Paranhos
Keywords: Polymeric membrane; nanocomposite; fuel cell; polymeric electrolyte
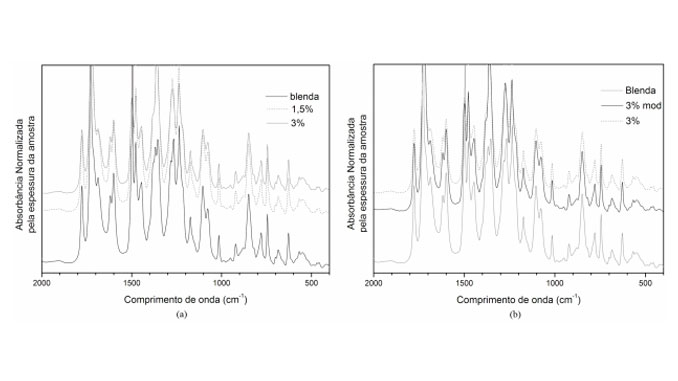
Abstract: Fuel Cells based in polymeric membranes are an alternative for the conventional energetic matrices based on fossil fuel and generation of energy with minimum environmental impact. However, polymeric membranes available nowadays for this specific use have some disadvantages, like low efficiency and cell durability. The aim of this work was to prepare and to characterize hybrid polymeric membranes for application as hydrogen fuel cell electrolytes. Membranes based in poly(ether imide) were chemically modified with sulfur groups to increase their ionic conductivity. The incorporation of mineral clay in nanometric scale aims to increase their mechanical and thermal properties. The membranes were evaluated by FTIR, DSC, TGA, DMA, density, hot water uptake, water vapor transmission and ionic migration resistance. The results leaded to a better structure versus properties balance, aiming the high performance of the obtained membranes.
DOI: 10.1590/0104-1428.1131