Writers: Maria T. Fabbro, Lourdes Gracia, Gabriela S. Silva, Luís P.S. Santos, Juan Andrés, Eloisa Cordoncillo, E. Longo
Keywords: Ag2CrO4; Order-disorder effects; Electron beam irradiation; Density-functional-theory
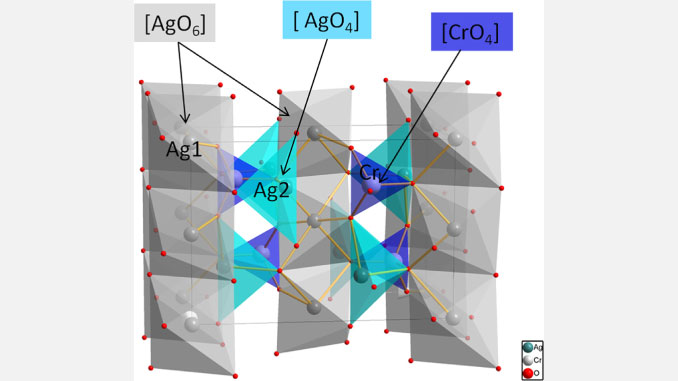
Abstract: Ag2CrO4 microcrystals were synthesized using the co-precipitation method. These microcrystals were characterized through X-ray diffraction (XRD) with Rietveld analysis, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), micro-Raman (MR). XRD patterns and Rietveld refinement data showed that the material exhibits an orthorhombic structure without any deleterious phases. FE-SEM and TEM micrographs revealed the morphology and the growth of Ag nanoparticles on Ag2CrO4 microcrystals during electron beam irradiation. These events were directly monitored in real-time. Their optical properties were investigated using ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) diffuse reflectance spectroscopy that allowed the calculation of the optical band gap energy. Theoretical analyses based on the density functional theory level indicate that the incorporation of electrons is responsible for structural modifications and formation of defects on the [AgO6] and [AgO4] clusters, generating ideal conditions for the growth of Ag nanoparticles.




