Microparticulated and nanoparticulated zirconium oxide added to calcium silicate cement: Evaluation of physicochemical and biological properties
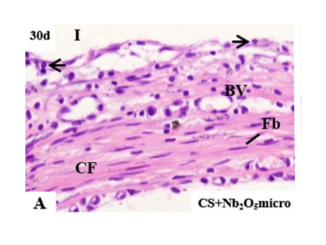
Abstract: The physicochemical and biological properties ofcalcium silicate-based cement (CS) associated to microparti-culated (micro) or nanoparticulated (nano) zirconium oxide(ZrO2) were compared with CS and bismuth oxide (BO) withCS. The pH, release of calcium ions, radiopacity, setting time,and compression strength of the materials were evaluated.The tissue reaction promoted by these materials in the sub-cutaneous was also investigated by morphological, immuno-histochemical, and quantitative analyses. For this purpose,polyethylene tubes filled with materials were implanted intorat subcutaneous. After 7, 15, 30, and 60 days, the tubes sur-rounded by capsules were fixed and embedded in paraffin. Inthe H&E-stained sections, the number of inflammatory cells(ICs) in the capsule was obtained. Moreover, detection ofinterleukin-6 (IL-6) by immunohistochemistry and number ofIL-6 immunolabeled cells were carried out. von Kossamethod was also performed. The differences among thegroups were subjected to Tukey test (p 0.05). The solutionscontaining the materials presented an alkaline pH andreleased calcium ions. The addition of radiopacifiersincreased setting time and radiopacity of CS. A higher com-pressive strength in the CS 1 ZrO2(micro and nano) wasfound compared with CS 1 BO. The number of IC and IL-6positive cells in the materials with ZrO2was significantlyreduced in comparison with CS 1 BO. von Kossa-positivestructures were observed adjacent to implanted materials.The ZrO2associated to the CS provides satisfactory physico-chemical properties and better biological response than BO.Thus, ZrO2may be a good alternative for use as radiopacify-ing agent in substitution to BO.
Author(s): Silva, Guilherme F.; Bosso, Roberta; Ferino, Rafael V.; et al.
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A
Volume: 102 Issue: 12 Pages: 4336-4345 Published: 2014
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.35099