Evidence for topological behavior in superconducting CuxZrTe2-y
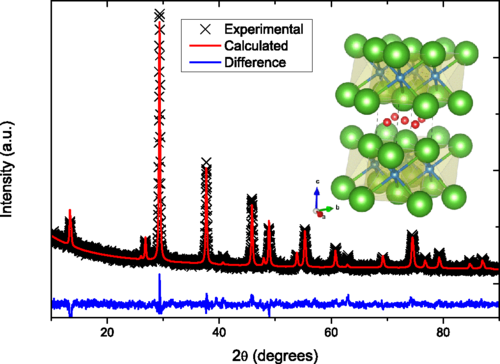
Abstract: We present structural, magnetic, electrical, thermal transport, Hall coefficient, and pressure-dependent resistivity measurements on C u x ZrT e 2 − y compounds with x = 0.05 , 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, and 0.3, and y varied between 0 ≤ y ≤ 0.8 . In order to calculate the ground state, ab initio calculations of the electronic structure of these materials were performed. Our results show that copper intercalation in ZrT e 2 induces superconductivity in the ZrT e 2 system. For the C u 0.3 ZrT e 1.2 sample, Hall and Seebeck coefficient measurements show that the system is predominantly negatively charged with carrier density close to 10 19 c m − 3 . The temperature dependence of the Hall coefficient, the Seebeck coefficient, and the lower critical field indicates that this material presents multiband character. Pressure-dependent resistivity vs temperature measurements reveal that while the normal-state resistivity decreases with increasing applied pressure, the superconducting transition temperature is completely insensitive to the applied pressure (for pressure in the range 0–1.3 GPa). This suggests that the Fermi gas is intrinsically degenerate under very high pressure, and therefore does not change much with varying external pressure. Finally the band structure calculation shows a dispersion curve containing a bulk three-dimensional Dirac conelike feature at the L point in the Brillouin zone, which is gapless in the absence of spin-orbit coupling, but develops a gap when this coupling is considered. Altogether, the results indicate that the superconducting compound C u x ZrT e 2 − y presents a signature of multiband behavior and may possibly be a new example of a topological superconductor.
Author(s): Machado, A. J. S.; Baptista, N. P.; de Lima, B. S.; et al.
Physical Review B
Volume: 95 Issue: 14 Published: 2017
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.95.144505
PDF: Evidence for topological behavior in superconducting CuxZrTe2-y




