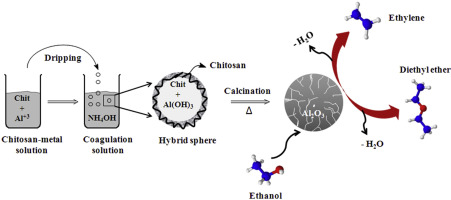
Simple synthesis of Al2O3 sphere composite from hybrid process with improved thermal stability for catalytic applications
Abstract: Aluminium oxide spheres were synthesized by the hybrid process applying the biopolymer chitosan. After the calcination process the porous spheres were characterized by Chemical elemental analysis (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, infrared spectroscopy (IR), and CO2 temperature programmed desorption (CO2-TPD). The effect of thermal treatment on surface properties of the oxide spheres was also evaluated by the catalytic ethanol dehydration reaction. The hybrid method produced interesting results related to the thermal stability against sintering process and consequently low decreases of surface area. The hybrid spheres calcination at 900 and 1200 °C produced a metastable phases of alumina with a high surface area, and nanometric crystallites. Additionally, the spheres of mixed silica-alumina synthesized by this method reveal the formation of porous spheres with highly acidic OH groups, which was suggested by the catalytic performance.
Author(s): Santos, Regina C. R.; Pinheiro, Antonio N.; Leite, Edson R.; et al.
Materials Chemistry and Physics
Volume: 160 Pages: 119-130 Published: 2015
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.04.014