Local structure and photoluminescence properties of nanostructured Zn1-xMnxS material
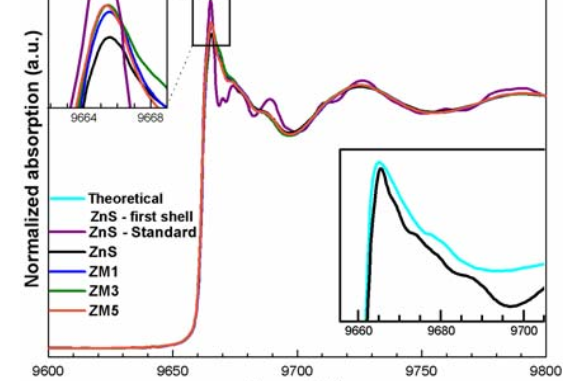
Abstract: Zinc sulfide (ZnS) pure or doped has received remarkable attention because of fundamental properties, versatility and potential for several technological applications as luminescent material. In this study, the local structure and photoluminescence properties of nanostructured Zn1-xMnxS samples have been characterized. X-ray diffraction results show that ZnS:Mn samples crystallized completely without the presence of secondary phases and the diffraction patterns correspond to the cubic zinc blende. Theoretical and experimental XANES (X-ray absorption near edge structure) spectra at Zn K-edge suggest the incorporation of Mn atoms into the ZnS host and indicate the occurrence of Zn and S vacancies, which are confirmed by EXAFS (extended X-ray absorption fine structure) fit results. These vacancies can be related to a red-shift observed in the peak emission of photoluminescence spectrum for ZnS sample, which is centered at similar to 504 nm. As the Mn content increases, a yellow-orange emission centered at similar to 590 nm can be observed besides the blue-green emission, which is associated with the T-4(1)-(6)A(1) transition within the 3d shell of Mn2+. (C) 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Author(s): Curcio, AL; Bernardi, MIB; Mesquita, A
PHYSICA STATUS SOLIDI C: CURRENT TOPICS IN SOLID STATE PHYSICS, VOL 12, NO 12
Volume: 12 Pages: 1367-1371 Published: MAY 11-15, 2015
PDF: Local structure and photoluminescence properties of nanostructured Zn1-xMnxS material
DOI: 10.1002/pssc.201510135