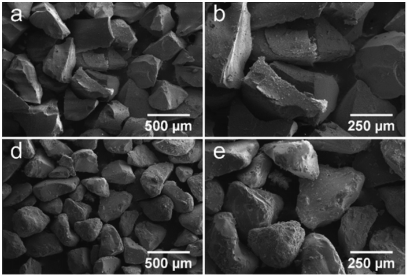
Abstract: The aim of this study was determinate the best sonochemical time in order to obtain better bone characteristics when a bioactive material (Biogran) is used in the filling periimplantar defects. In this study, 32 rats were submitted to surgical proceedings to create a periimplantar defect that was filled with Biogran receiving different sonochemical times: 15 (G1), 30 (G2), 45 (G3) or 90 min (G4). The biomaterial was characterized through X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). In vivo analysis was performed through micro CT, laser confocal microscopy, immunohistochemistry and evaluation of bone cytoarchitecture through hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. The data were submitted to statistical testing, considering a significance level of p < 0.05. Rx diffraction of pure bioglass showed that it is predominantly amorphous; otherwise, there are small peaks at 23 degrees and 31 degrees. SEM shows that the longer the sonochemical time, the less edges the biomaterial will present. Within the groups, G1 and G2 showed the best quantity and quality by micro CT (p > 0.05). The best bone turnover result was found in G1 and G2, otherwise the better results were related to neoformed bone area, bone mineral apposition rate and bone implant contact to G1 (p < 0.05). G1 had the best results in terms of bone cytoarchitectural evaluation and immunohistochemistry. It is possible to conclude that Biogran that received 15 min of sonochemical treatment (G1) presented periimplantar bone repair with the best extracellular matrix properties, including the best quality and quantity of vital bone.
Author(s): Gomes-Ferreira, PHS; Lisboa, PN; da Silva, AC; Bim, O; Batista, FRD; Ervolino-Silva, AC; Garcia, IR; Okamoto, R
ULTRASONICS SONOCHEMISTRY
Volume: 56 Pages: 437-446 Published: SEP 2019
PDF: Sonochemical time standardization for bioactive materials used in periimplantar defects filling
DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.04.032
