Photoluminescence and X-ray induced scintillation in Gd3+-modified fluorophosphate glasses doped with Ce3+
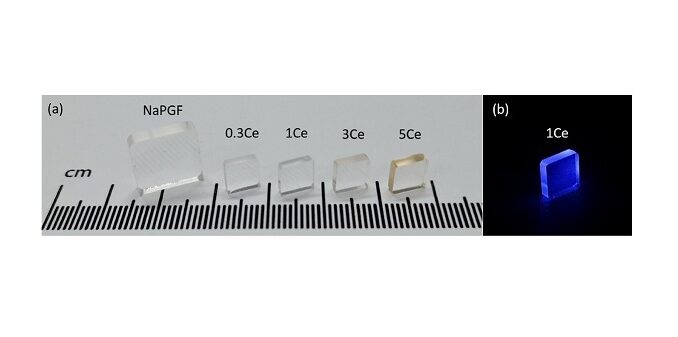
Abstract: In this work, we report the fabrication of Gd3+-modified fluorophosphate glasses doped with Ce3+ with the new compositions 50NaPO3–20BaF2-(10-x)CaF2-20GdF3-xCeCl3, x = 0.3; 1; 3 and 5 mol% and their promising features as scintillators. The glasses present high molar density values (ρ ≅ 4 g cm−3), comparable to that of crystal scintillators, and distinguished optical properties. By UV–visible absorption, photoluminescence emission and excitation, excited state decay curves and radioluminescence measurements, the photophysical properties of the glasses were fully characterized. In addition, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was employed to confirm the valence state of Ce ions. The results of emission spectra measured in the visible range upon UV excitation together with the excited state lifetime values of Ce3+ (5d → 4f transition) and Gd3+ (8S7/2→6Ij transition) clearly evidence energy transfer (ET) from the latter to the former ion. Though not quantified, the ET favors the fast decaying (τ = 24 ns) efficient emission of Ce3+ which makes the materials promising for fast response high energy radiation detectors. The response to X-ray excitation associated with the relatively high molar density of the glasses, indicate the promising application of these glasses for medical diagnosis where, in particular, a fast and intense response under high-energy radiation excitation is crucial.
Author(s): Galleani, G.; Lodi, T. A.; Mastelaro, V. R.; Jacobsohn, L. G.; de Camargo, A. S. S.
Optical Materials
Published: November 2022, Volume 133, 112934
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112934
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).