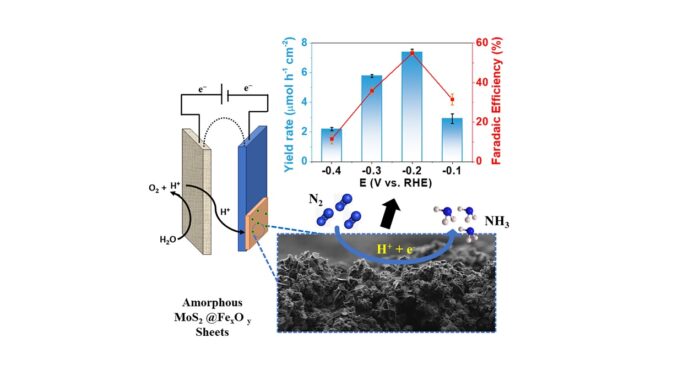
Enhancing electrochemical N2 reduction at mild conditions with FexOy co-deposited on amorphous MoS2
Abstract: Electrochemical reduction of N2 can lead to the clean and sustainable production of NH3 under environmental conditions. However, limited progress has been made as most catalysts lack efficient activity for N2 fixation. Here, we report FexOy co-deposited on amorphous MoS2 supported on a gas diffusion layer electrode (GDL) as an effective catalyst for N2 reduction. The catalysts were prepared by electrodeposition, a simple and low-cost method. Physical characterizations revealed the amorphous nature of MoS2 and while FexOy was evenly distributed over MoS2. In 0.1 M Na2SO4, GDL/MoS2-Fe-1 exhibited an NH3 yield of 7.38 µmol h−1 cm−2, a value almost 2 times greater than that obtained for MoS2/GDL and a faradaic efficiency of 54.9 % at ˗0.2 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) at 25 ℃. Also, the catalyst displayed high stability and durability, retaining almost 93 % of its original values after recycling tests. The amorphous MoS2-FexOy provides new insight into designing efficient and robust catalysts for nitrogen reduction.
Author(s): Caio V.S. Almeida, Lucia H. Mascaro
Electrochimica Acta
Volume 476, 1 February 2024, 143680
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2023.143680
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).