Online near-infrared spectroscopy for automatic polymeric material identification
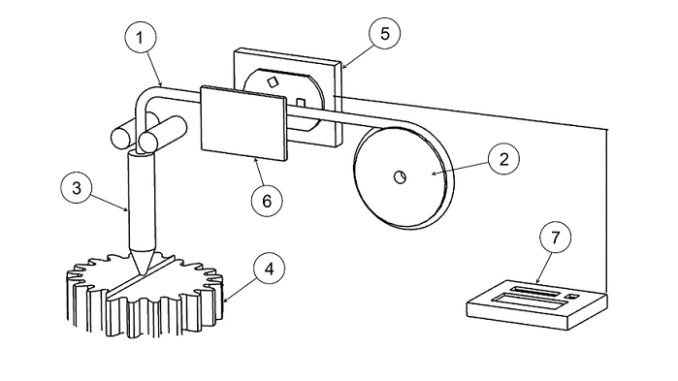
Abstract: Additive manufacturing (AM) offers several advantages for transforming productive chains, such as generation of complex geometries on demand. However, challenges must be overcome toward increasing manufacturing precision and quality of the parts produced, reducing production time, and standardizing the processing parameters. One example of common failure is the incorrect processing parameter selection for the filament-based AM, which can damage 3D printing machines, such as hotend clogging. In that way, this paper introduces a method that identifies AM’s polymeric materials through in situ near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy and classifies them into poly(lactic acid), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, and poly(ethylene glycol terephthalate), also enabling a manual parameter input. A low-cost NIR spectrophotometer was used to analyze 16 filaments with color and manufacturer variability. Each filament was probed 3 times in 3 distinct places, raising 144 spectra. Chemometrics were applied to identify relevant peaks for functional groups, and a linear regression was used to filter out data that showed no such peaks. In a second stage, a second-derivative Savitzky–Golay was used to aid in class separation, and a principal component analysis was performed to reduce data dimensionality. The resulting projections were classified by an LDA algorithm, and 3 study cases conducted with data augmentation tested the classifier. The results show the proposed method is robust to bias variation and can handle blends of up to 70%–30% mix and correctly separate signals with and without peaks. Such responses have proved the feasibility of the classification system, especially when fed with a highly varied data set.
Author(s): da Cunha, D. A. L. V.; Ribessi, R. L.; Hernandes, A. C.; Raimundo, I. M., Jr.; Aroca, R. V.; Branciforti, M. C.
Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering
Published: 14 July 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-022-03645-1
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).