Computational Modeling for the Ag Nanoparticle Coalescence Process: A Case of Surface Plasmon Resonance
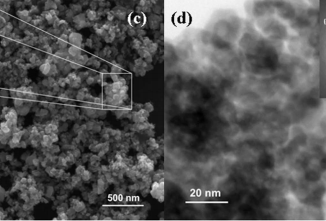
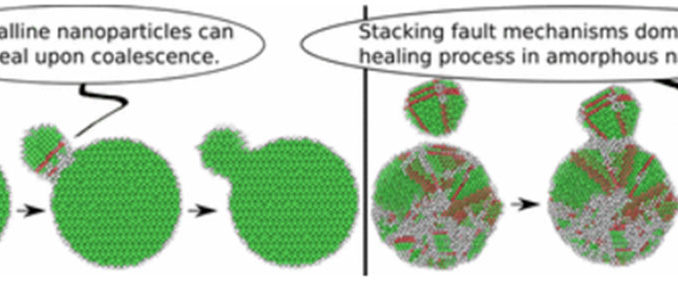
Abstract: Motivated by recent transmission electron microscopy (TEM) experiments on α-Ag2WO4, the coalescence process of Ag nanoparticles (NPs) is investigated using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. These Ag NPs are formed by irradiation of α-Ag2WO4 crystals by electrons from a TEM gun. This behavior can be considered as a clear example of surface plasmon resonance (SPR), in which Ag NP coalescence processes are controlled by dipole–dipole interaction forming larger clusters. The interactions between Ag NPs along the coalescence processes are studied using MD simulations with embedded atom method (EAM) effective potentials for Ag. With these choices of methods, coalescence is studied by addressing different scenarios for the interacting NPs, which all could possibly occur in experiments.
Authors: Giovani M. Faccin, Miguel A. San-Miguel, J. Andres, E. Longo, E. Z. da Silva.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
2017, 121 (12), pp 7030–7036
Link: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00769
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00769