In situ microwave-enhanced electrochemical reactions at stainless steel: Nano-iron for aqueous pollutant degradation
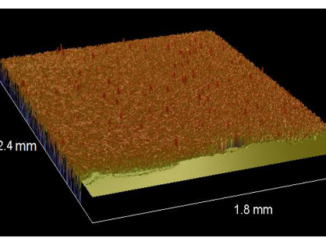
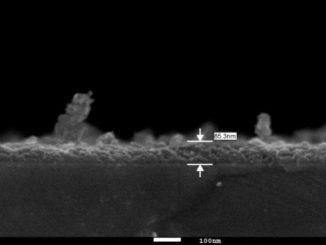
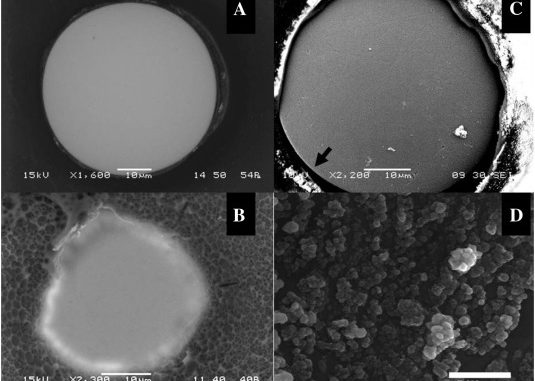
Abstract: Iron nanoparticle deposition and stripping are observed from aqueous Fe2 + solution at pH 3 on stainless electrodes in the presence of focused microwave activation. The effects of Fe2 + concentration and microwave power are evaluated. It is shown that the resulting iron nanoparticle deposit (i) gives well-defined anodic stripping responses, (ii) is readily released into the solution phase, and (iii) is highly reactive towards chlorinated hydrocarbons such as trichloroacetate. The combined effects of increased mass transport and localized microwave heating improve pollutant degradation treatments.
Author(s): Cabello, Gema; Gromboni, Murilo F.; Pereira, Ernesto C.; et al.
Electrochemistry Communications
Volume: 62 Pages: 48-51 Published: 2016
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2015.11.007