Zirconium oxide and niobium oxide used as radiopacifiers in a calcium silicate-based material stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen formation
Abstract: Aim To evaluate the influence of the addition of microparticulate (micro) and nanoparticulate (nano) zirconium oxide (ZrO2) and niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5) to a calcium silicate-based cement (CS) on the subcutaneous healing process in rats compared with MTA Angelus.
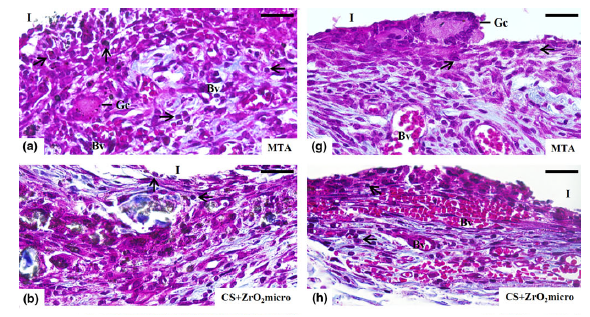
Methodology In each rat, two polyethylene tubes filled with the following materials: (i) MTA; (ii) CS+ ZrO(2)micro; (iii) CS+ZrO(2)nano; (iv) CS+Nb(2)O(5)micro or (v) CS+Nb(2)O(5)nano were implanted subcutaneously; empty polyethylene tubes were used in the Control group. After 7, 15, 30 and 60days, the specimens (n=5 per group in each period) were fixed and embedded in paraffin. Masson’s trichrome sections were used to obtain the volume density of the inflammatory cells (VvIC) and fibroblasts (VvFb). The sections were also stained with Picrosirius-red to calculate the birefringent collagen content. Fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF-1) was detected by immunohistochemistry, and the number of immunolabelled cells was obtained. The data were subjected to two-way anova followed by Tukey’s test (P0.05).
Results At all periods, the VvIC was significantly lower (P<0.001) in all the CS and Control groups than in the MTA group. At all periods, the VvFb was reduced significantly (P=0.023) in the MTA group in comparison with the other groups. In addition, the number of immunolabelled cells in the capsules of the CS groups was significantly higher (P<0.001) than in the MTA group at all time-points.
Conclusions The experimental materials (CS+ ZrO2 and CS+Nb2O5) induced fibroblast proliferation and accelerated the regression of the inflammatory reaction. However, the addition of nanoparticulate radiopacifiers did not improve the biological properties of a calcium silicate-based cement when compared to microparticulate agents.
Author(s): Silva, G. F.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J. M.; da Fonseca, T. S.; et al.
International Endodontic Journal
Volume: 50 Pages: E95-E108 Published: 2017
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12789