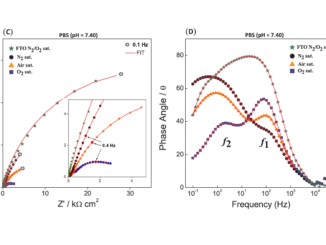
In-Depth Understanding of the Relation between CuAlO2 Particle Size and Morphology for Ozone Gas Sensor Detection at a Nanoscale Level
Abstract:
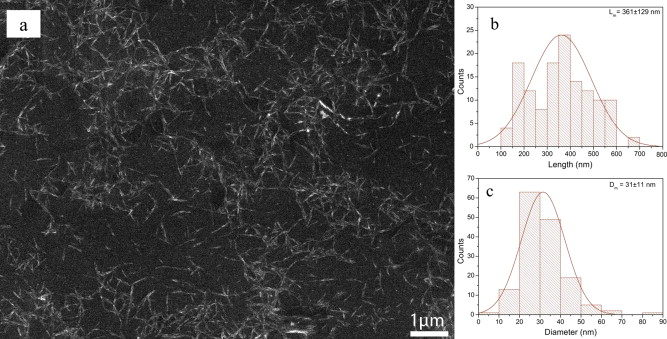
Cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) were prepared by sulfuric acid hydrolysis from cotton microfibers, and used to prepare polyurethane (PU) nanocomposites by mixing CNFSand PU water suspensions. CNFs as nanofillers improved the tensile strength of PU significantly up to 10 wt% content. With an increase in the CNF content, the glass transition temperature of PU and the temperature onset of the soft segment increased compared with those of neat PU. However, the crystalline phase present in soft domains and its melting temperature decreased. The influences of humidity on the mechanical properties of PU/CNF nanacomposites were also investigated. The tensile strength at different elongations of PU/CNF nanocomposites decreased substantially after being exposed to 60% relative humidity for 24 h; for 10 wt% loading, the tensile strength at 500% dropped from 10.64 to 2.34 MPa. This behavior was attributed to the formation of hydrogen bonds of PU and CNFs with water.
Author(s): Thirumalairajan, S.; Mastelaro, Valmor R.; Escanhoela, Carlos A., Jr.
Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces
Volume: 6 Issue: 23 Pages: 21739-21749 Published: 2014
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.08.013