Impact of the Alkali Cation on the Oscillatory Electro-Oxidation of Ethylene Glycol on Platinum
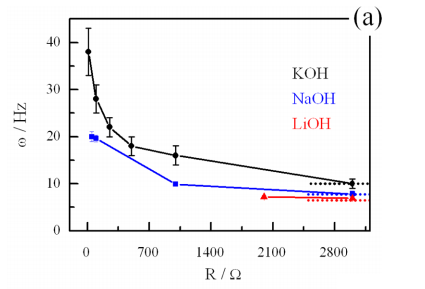
Abstract: We report the effect of alkali cation (Li+, Na+, and K+) on the oscillatory electro-oxidation of ethylene glycol in alkaline media. As experimentally verified, the nature of the alkali cation strongly impacts the waveform and frequency of the potential oscillations. The oscillation frequencies decrease in the order KOH > NaOH > LiOH, which also corresponds to the ascending order of the surface blockage due to the noncovalent interactions. On the other hand, the estimated rate constant of poison formation, k(p), under oscillatory regime is higher in the presence of KOH rather than NaOH, both acting as the supporting electrolytes. In order to shed light on the relationships between the kinetic and dynamical features, we performed numerical simulations based on a generic model which includes the time evolution of cation coverage. Overall, we were able to reproduce the major features observed experimentally; k(p) was assigned to the electrochemical steps of C-C bond breaking instead of direct noncovalent interactions between the hydrated alkali cation and surface oxides. Finally, the results are rationalized in terms of the cation influence on the feedback loops and of the underlying surface chemistry.
Author(s): Sitta, E; Nagao, R; Kiss, IZ; Varela, H
JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY C
Volume: 119 Pages: 1464-1472 Published: JAN 22 2015
PDF: Impact of the Alkali Cation on the Oscillatory Electro-Oxidation of Ethylene Glycol on Platinum
DOI: 10.1021/jp5105505