Effect of the electrodeposition potential on the photoelectroactivity of the SnS/Sb2S3 thin films
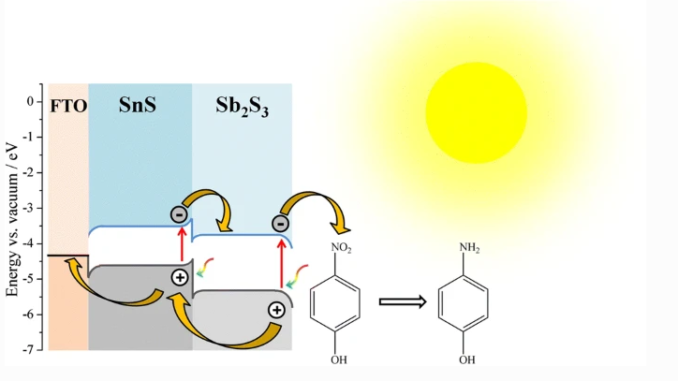
Abstract: The present work outlines a simple and novel approach to obtain nanostructured and heterostructured SnS/Sb2S3 thin films. This material showed enhanced photoelectroactivity in comparison to the individual tin (II) sulphide (SnS) and antimony (III) sulphide (Sb2S3) films. These nanostructured films were grown by electrodeposition of antimony tin (SbSn) compound followed by sulphurisation under a sulphur vapour atmosphere. The optimisation of the growth methodology was systematically performed by evaluating the photoelectroactivity of the films prepared at different deposition potentials as well as by characterisation of the as-deposited binary compound and the films after sulphurisation. In comparison to the individual SnS and Sb2S3 films, the SnS/Sb2S3 one presented a photocurrent response increased 10-fold compared to the former and 48-fold compared to the latter. Further studies carried out by Mott-Schottky analysis and band gap determination confirmed that the band edge positions of the single SnS and Sb2S3 phases are suitably aligned, forming a type II heterostructure which facilitates minority carriers’ separation and transportation and therefore improves the photocurrent density values.
Author(s): Araújo,MA; Lucas, FWS; Mascaro, LH
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry
Published: 30 January 2020