Boosting the Photocurrent of the WO3/BiVO4 Heterojunction by Photoelectrodeposition of the Oxy-Hydroxide-Phosphates Based on Co, Fe, or Ni
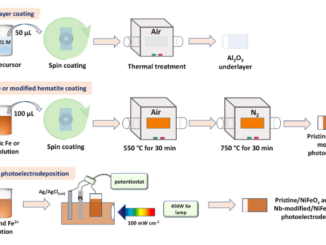
Abstract: Here we investigated the photoelectrodeposition of oxygen-evolving catalysts (OECs) based on oxy-hydroxides-phosphates of Co, Fe, or Ni (CoPi, FePi, and NiPi) on the WO3/BiVO4 heterojunction and their activity in water oxidation. The OECs were deposited by cycles of (i) open-circuit potential (OCP) and (ii) applying a potential positive enough to oxidize the metallic precursor on the WO3/BiVO4. The crystalline and optical properties of the photoanodes were not significantly affected by the OECs deposition. However, there was a remarkable increase in the photocurrent densities (jpc) to water oxidation, where the modification with FePi showed the best result, achieving 2.12 mA cm−2, which corresponds to 2.83 times higher than the heterojunction without the OECs. Furthermore, the OECs deposition changed the morphology of the heterojunction with the deposition of a thin film on its surface. In addition, during the FePi deposition, the BiVO4 layer seems to partially dissolve. Our study shows a facile methodology to boost the activity of photoanodes to the water oxidation by photoelectrodeposition of OECs.
Author(s): Coelho, D.; Gaudêncio, J.P.R. S. ; Mascaro, L.H.
J. Braz. Chem. Soc.
Published: January 18, 2022
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20220015
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).