Enhancement of the ozone-sensing properties of ZnO through chemical-etched surface texturing
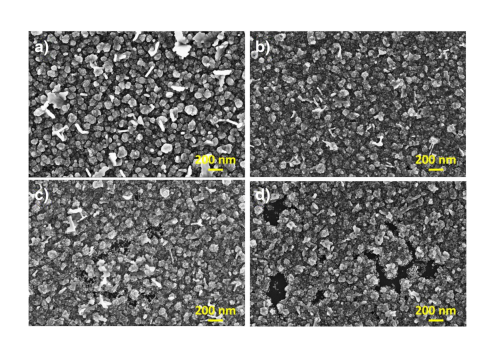
Abstract: Semiconductor metal oxides (SMOx) are widely studied for different applications. It is well established that the gas-SMOx interaction strongly depends on the charge exchange between the exposed surface area and the target gas. Hence, nanostructuring processes can amplify these surface effects and enhance SMOx sensitivity. Recently, different studies have demonstrated that nanostructured ZnO-based devices exhibit improved efficiency by chemical etched surface texturing using diluted hydrochloric acid (HCl) solutions. In this context, this study investigates the influence of chemical etching by HCl on the gas-sensing properties of ZnO thin films regarding ozone (O3) detection. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis suggested an increase in the density of surface defects in the etched samples, leading to a higher density of adsorption sites for gas molecules. Scanning electron microscopy images before and after acid immersion revealed an increase in the surface area as the average grain size decreases and the film’s porosity increases. Measurements of the gas-sensing properties operating at 300 °C showed that the nanostructuring process significantly enhances the sensitivity of ZnO thin films for O3 detection, indicating a synergic effect between the grain size decrease and the porosity increase. Our results demonstrate that this methodology can be used to enhance the sensitivity of SMOx-based gas sensors.
Author(s): Silva, W. A. D.; de Lima, B. S.; Bernardi, M. I. B.; Mastelaro, V. R.
Journal of Nanoparticle Research
Published: 09 May 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05479-3
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).