Tungsten gallium-phosphate glasses as promising intrinsic scintillators
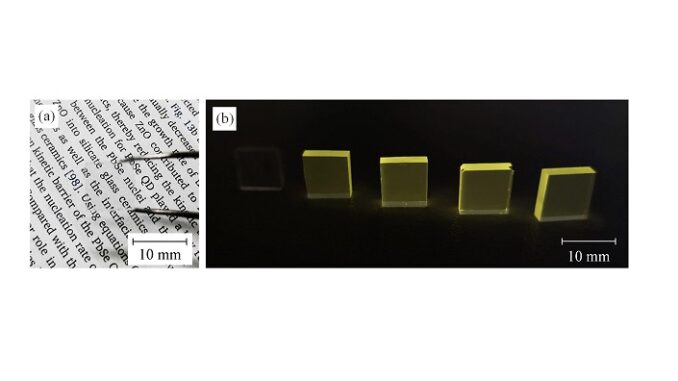
Abstract: Tungsten gallium-phosphate glasses with composition NaPO3-20Ga2O3-xNa2WO4 (x = 0, 1, 3, 5 and 10% mol) were synthesized by the melt-quenching technique with high chemical stability and excellent optical properties, and evaluated as potential intrinsic glass scintillators. Fourier-transform infrared measurements showed a decrease in the amount of OH- groups for increasing Na2WO4 contents, while X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed the presence of sole W6+ species. Optical transmission measurements showed a high level of transmittance (∼90%) over a broad spectral range (400 to 2500 nm). Luminescence was found to correspond to a broad emission characteristic of the WO42− complex that can be excited by ultraviolet and X-rays with average lifetimes ranging from 32 to 20 μs. At cryogenic temperatures, the NaPGaW glasses showed a significant increase in the luminescence emission.
Author(s): Lodi, T. A.; Galleani, G.; Merizio, L. G.; Jacobsohn, L. G.; Mastelaro, V. R.; de Camargo, A. S.
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids
Published: 1 March 2023, Volume 603, 122097
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.122097
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).